Group PJMEDIA_PORT
- group PJMEDIA_PORT
Extensible framework for media terminations.
Media Port Concepts
Media Port
A media port (represented with pjmedia_port “class”) provides a generic and extensible framework for implementing media elements. Media element itself could be a media source, sink, or processing element. A media port interface basically has the following properties:
media port information (pjmedia_port_info) to describe the media port properties (sampling rate, number of channels, etc.),
optional pointer to function to acquire frames from the port (the
get_frame()interface), which will be called by pjmedia_port_get_frame() public API, andoptional pointer to function to store frames to the port (the
put_frame()interface) which will be called by pjmedia_port_put_frame() public API.
The
get_frame()andput_frame()interface of course would only need to be implemented if the media port emits and/or takes media frames respectively.Media ports are passive “objects”. By default, there is no worker thread to run the media flow. Applications (or other PJMEDIA components, as explained in Clock/Timing) must actively call pjmedia_port_get_frame() or pjmedia_port_put_frame() from/to the media port in order to retrieve/store media frames.
Some media ports (such as Conference Bridge and Resample Port) may be interconnected with (or encapsulate) other port, to perform the combined task of the ports, while some others represent the ultimate source/sink termination for the media. Interconnection means the upstream media port will call
get_frame()andput_frame()to its downstream media port. For this to happen, the media ports need to have the same format, where format is defined as combination of sample format, clock rate, channel count, bits per sample, and samples per frame for audio media.Example: Manual Resampling
For example, suppose application wants to convert the sampling rate of one WAV file to another. In this case, application would create and arrange media ports connection as follows:
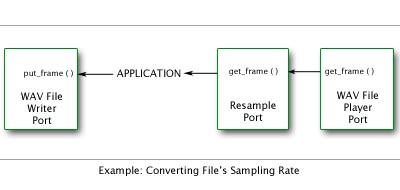
Application would setup the media ports using the following pseudo- code:
pjmedia_port *player, *resample, *writer; pj_status_t status; // Create the file player port. status = pjmedia_wav_player_port_create(pool, "Input.WAV", // file name 20, // ptime. PJMEDIA_FILE_NO_LOOP, // flags 0, // buffer size NULL, // user data. &player ); PJ_ASSERT_RETURN(status==PJ_SUCCESS, PJ_SUCCESS); // Create the resample port with specifying the target sampling rate, // and with the file port as the source. This will effectively // connect the resample port with the player port. status = pjmedia_resample_port_create( pool, player, 8000, 0, &resample); PJ_ASSERT_RETURN(status==PJ_SUCCESS, PJ_SUCCESS); // Create the file writer, specifying the resample port's configuration // as the WAV parameters. status pjmedia_wav_writer_port_create(pool, "Output.WAV", // file name. resample->info.clock_rate, resample->info.channel_count, resample->info.samples_per_frame, resample->info.bits_per_sample, 0, // flags 0, // buffer size NULL, // user data. &writer);
After the ports have been set up, application can perform the conversion process by running this loop:
pj_int16_t samplebuf[MAX_FRAME]; while (1) { pjmedia_frame frame; pj_status_t status; frame.buf = samplebuf; frame.size = sizeof(samplebuf); // Get the frame from resample port. status = pjmedia_port_get_frame(resample, &frame); if (status != PJ_SUCCESS || frame.type == PJMEDIA_FRAME_TYPE_NONE) { // End-of-file, end the conversion. break; } // Put the frame to write port. status = pjmedia_port_put_frame(writer, &frame); if (status != PJ_SUCCESS) { // Error in writing the file. break; } }
For the sake of completeness, after the resampling process is done, application would need to destroy the ports:
// Note: by default, destroying resample port will destroy the // the downstream port too. pjmedia_port_destroy(resample); pjmedia_port_destroy(writer);
The above steps are okay for our simple purpose of changing file’s sampling rate. But for other purposes, the process of reading and writing frames need to be done in timely manner (for example, sending RTP packets to remote stream). And more over, as the application’s scope goes bigger, the same pattern of manually reading/writing frames comes up more and more often, thus perhaps it would be better if PJMEDIA provides mechanism to automate this process.
And indeed PJMEDIA does provide such mechanism, which is described in Clock/Timing section.
Automating Media Flow
PJMEDIA provides few mechanisms to make media flows automatically among media ports. This concept is described in Clock/Timing section.
Defines
-
DEPRECATED_FOR_TICKET_2251
-
PJMEDIA_PORT_SIG(a, b, c, d)
Create 32bit port signature from ASCII characters.
Enums
-
enum pjmedia_port_op
Port operation setting.
Values:
-
enumerator PJMEDIA_PORT_NO_CHANGE
No change to the port TX or RX settings.
-
enumerator PJMEDIA_PORT_DISABLE
TX or RX is disabled from the port. It means get_frame() or put_frame() WILL NOT be called for this port.
-
enumerator PJMEDIA_PORT_MUTE
TX or RX is muted, which means that get_frame() or put_frame() will still be called, but the audio frame is discarded.
-
enumerator PJMEDIA_PORT_ENABLE
Enable TX and RX to/from this port.
-
enumerator PJMEDIA_PORT_NO_CHANGE
Functions
-
unsigned PJMEDIA_PIA_SRATE(const pjmedia_port_info *pia)
Utility to retrieve audio clock rate/sampling rate value from pjmedia_port_info.
- Parameters:
pia – Pointer to port info containing audio format.
- Returns:
Audio clock rate.
-
unsigned PJMEDIA_PIA_CCNT(const pjmedia_port_info *pia)
Utility to retrieve audio channel count value from pjmedia_port_info.
- Parameters:
pia – Pointer to port info containing audio format.
- Returns:
Audio channel count.
-
unsigned PJMEDIA_PIA_BITS(const pjmedia_port_info *pia)
Utility to retrieve audio bits per sample value from pjmedia_port_info.
- Parameters:
pia – Pointer to port info containing audio format.
- Returns:
Number of bits per sample.
-
unsigned PJMEDIA_PIA_PTIME(const pjmedia_port_info *pia)
Utility to retrieve audio frame interval (ptime) value from pjmedia_port_info.
- Parameters:
pia – Pointer to port info containing audio format.
- Returns:
Frame interval in msec.
-
unsigned PJMEDIA_PIA_SPF(const pjmedia_port_info *pia)
This is a utility routine to retrieve the audio samples_per_frame value from port info.
- Parameters:
pia – Pointer to port info containing audio format.
- Returns:
Samples per frame value.
-
unsigned PJMEDIA_PIA_AVG_BPS(const pjmedia_port_info *pia)
This is a utility routine to retrieve the average bitrate value from port info.
- Parameters:
pia – Pointer to port info containing audio format.
- Returns:
Bitrate, in bits per second.
-
unsigned PJMEDIA_PIA_MAX_BPS(const pjmedia_port_info *pia)
This is a utility routine to retrieve the maximum bitrate value from port info.
- Parameters:
pia – Pointer to port info containing audio format.
- Returns:
Bitrate, in bits per second.
-
unsigned PJMEDIA_PIA_AVG_FSZ(const pjmedia_port_info *pia)
This is a utility routine to retrieve the average audio frame size value from pjmedia_port_info.
- Parameters:
pia – Pointer to port info containing audio format.
- Returns:
Frame size in bytes.
-
unsigned PJMEDIA_PIA_MAX_FSZ(const pjmedia_port_info *pia)
Utility to retrieve audio frame size from maximum bitrate from pjmedia_port_info.
- Parameters:
pia – Pointer to port info containing audio format.
- Returns:
Frame size in bytes.
-
pj_status_t pjmedia_port_info_init(pjmedia_port_info *info, const pj_str_t *name, unsigned signature, unsigned clock_rate, unsigned channel_count, unsigned bits_per_sample, unsigned samples_per_frame)
This is an auxiliary function to initialize port info for ports which deal with PCM audio.
- Parameters:
info – The port info to be initialized.
name – Port name.
signature – Port signature.
clock_rate – Port’s clock rate.
channel_count – Number of channels.
bits_per_sample – Bits per sample.
samples_per_frame – Number of samples per frame.
- Returns:
PJ_SUCCESS on success.
-
pj_status_t pjmedia_port_info_init2(pjmedia_port_info *info, const pj_str_t *name, unsigned signature, pjmedia_dir dir, const pjmedia_format *fmt)
This is an auxiliary function to initialize port info for ports which deal with PCM audio.
- Parameters:
info – The port info to be initialized.
name – Port name.
signature – Port signature.
dir – Port’s direction.
fmt – Port’s media format.
- Returns:
PJ_SUCCESS on success.
-
pjmedia_clock_src *pjmedia_port_get_clock_src(pjmedia_port *port, pjmedia_dir dir)
Get a clock source from the port.
- Parameters:
port – The media port.
dir – Media port’s direction.
- Returns:
The clock source or NULL if clock source is not present in the port.
-
pj_status_t pjmedia_port_get_frame(pjmedia_port *port, pjmedia_frame *frame)
Get a frame from the port (and subsequent downstream ports).
- Parameters:
port – The media port.
frame – Frame to store samples.
- Returns:
PJ_SUCCESS on success, or the appropriate error code.
-
pj_status_t pjmedia_port_put_frame(pjmedia_port *port, pjmedia_frame *frame)
Put a frame to the port (and subsequent downstream ports).
- Parameters:
port – The media port.
frame – Frame to the put to the port.
- Returns:
PJ_SUCCESS on success, or the appropriate error code.
-
pj_status_t pjmedia_port_destroy(pjmedia_port *port)
Destroy port (and subsequent downstream ports).
Note that if the port has group lock, instead of destroying the port immediately, this function will just decrease the reference counter.
- Parameters:
port – The media port.
- Returns:
PJ_SUCCESS on success, or the appropriate error code.
-
pj_status_t pjmedia_port_init_grp_lock(pjmedia_port *port, pj_pool_t *pool, pj_grp_lock_t *glock)
This is a helper function to initialize the port’s group lock. This function will create a group lock if NULL is passed, initialize the group lock by adding the port’s destructor to the group lock handler list, and increment the reference counter.
This function should only be called by a media port implementation and after port’s on_destroy() function has been assigned.
- Parameters:
port – The pjmedia port to be initialized.
pool – The pool, this can be a temporary pool as group lock will create and use its internal pool.
glock – The group lock, or create a new one if NULL.
- Returns:
PJ_SUCCESS on success, PJ_EEXISTS if group lock is already initialized, or the other appropriate error code.
-
pj_status_t pjmedia_port_add_ref(pjmedia_port *port)
This is a helper function to increase the port reference counter.
- Parameters:
port – The PJMEDIA port.
- Returns:
PJ_SUCCESS on success.
-
pj_status_t pjmedia_port_dec_ref(pjmedia_port *port)
This is a helper function to decrease the port reference counter.
- Parameters:
port – The PJMEDIA port.
- Returns:
PJ_SUCCESS on success.
-
struct pjmedia_port_info
- #include <port.h>
Port info.
Public Members
-
pj_uint32_t signature
Port signature.
-
pjmedia_dir dir
Port direction.
-
pjmedia_format fmt
Format.
-
pj_uint32_t signature
-
struct pjmedia_port
- #include <port.h>
Port interface.
Public Members
-
pjmedia_port_info info
Port information.
-
pj_grp_lock_t *grp_lock
Group lock.
This is optional, but if this port is registered to the audio/video conference bridge, the bridge will create one if the port has none.
-
pjmedia_clock_src *(*get_clock_src)(struct pjmedia_port *this_port, pjmedia_dir dir)
Get clock source. This should only be called by pjmedia_port_get_clock_src().
-
pj_status_t (*put_frame)(struct pjmedia_port *this_port, pjmedia_frame *frame)
Sink interface. This should only be called by pjmedia_port_put_frame().
-
pj_status_t (*get_frame)(struct pjmedia_port *this_port, pjmedia_frame *frame)
Source interface. This should only be called by pjmedia_port_get_frame().
-
pj_status_t (*on_destroy)(struct pjmedia_port *this_port)
Called to destroy this port.
-
struct port_data
- #include <port.h>
Port data can be used by the port creator to attach arbitrary value to be associated with the port.
-
pjmedia_port_info info